Definition
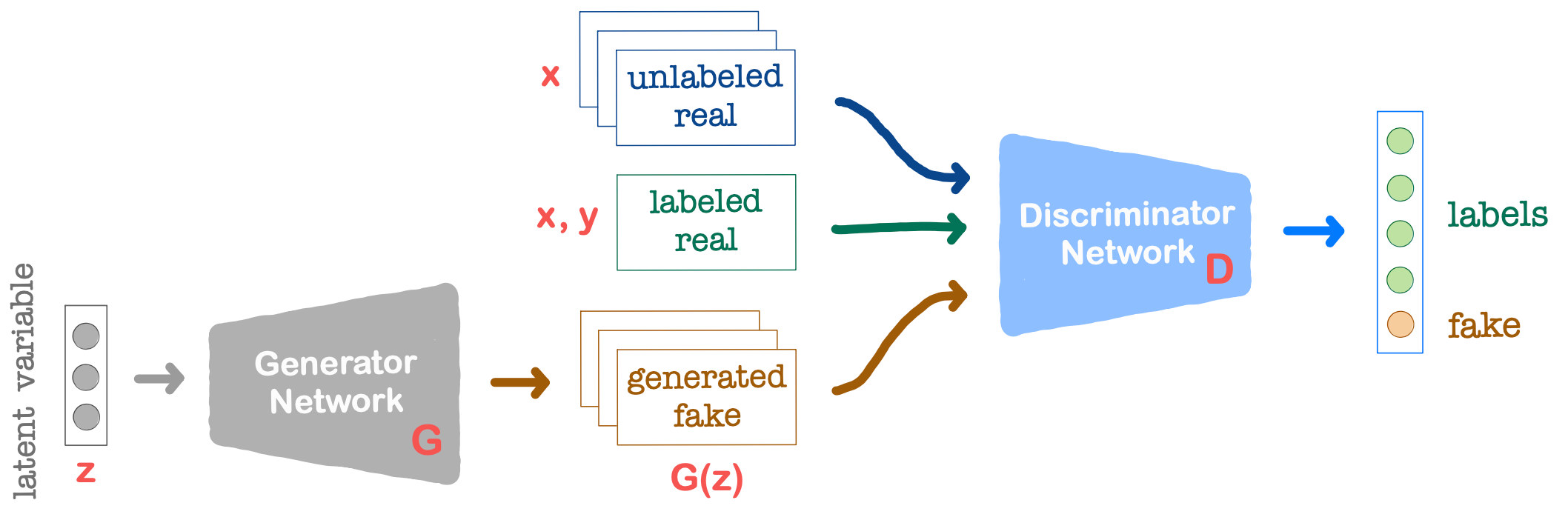
Semi-supervised GAN (SGAN) is a variation of the GAN that takes both labeled and unlabeled data in the training process. The model aims to create a data-efficient classifier and to improve the generating quality.
Architecture
Objective Function
The objective function of SGAN consists of four losses: supervised loss, unsupervised loss, generator loss, and feature matching loss. The supervised loss is calculated only for labeled samples, and aims to correctly classify the real samples into their correct class. The unsupervised loss is calculated for both unlabeled real samples and generated samples, and encourages the discriminator to distinguish between real and fake samples. The generator loss is used to ensure the generated images are realistic. The feature matching loss encourages the generator to produce samples have similar feature representation to real data in the discriminator’s intermediate layer.
Supervised loss: Unsupervised loss: Generator loss: Feature matching loss where:
- is the generator
- is the discriminator
- is the model’s predicted probability for the correct class.
- is the model’s predicted probability for the fake class.
- is the distribution of the labeled data
- is the distribution of the data (both labeled and unlabeled)
- is the distribution of noise
- is the intermediate layer of the discriminator
The full objective function for SGAN is defined as: where:
- and are the parameters of the generator and discriminator, respectively
- is a hyperparameter that controls the weight of the feature matching loss.