Definition
An interior point optimization technique used to solve constrained optimization problems. It involves adding a barrier or penalty term to the objective function that penalizes solutions for being outside the feasible region.
Algorithm
Consider the optimization problem with an inequality constraint
subject to
The KKT Conditions of the problem are the following
- ^[Stationarity]
- ^[Primal feasibility]
- ^[Dual feasibility]
- ^[Complementary slackness]
Interior point methods solve the problem whose complementary slackness condition is relaxed where
the stationary condition become where is called a logarithmic barrier function
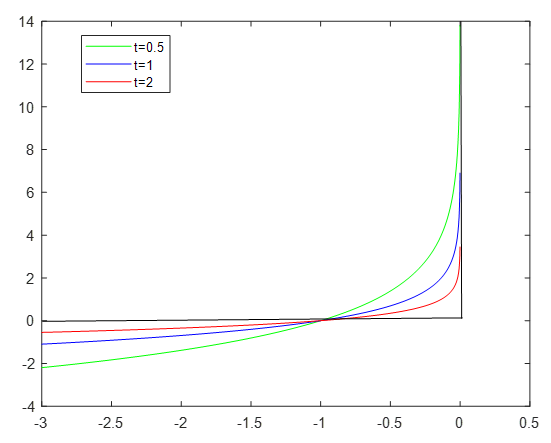 As large, the logarithmic barrier function functions like an indicator function.
As large, the logarithmic barrier function functions like an indicator function.
Now, by the definition of log function, should be negative or zero, so the primal feasibility condition holds. Also, by the relaxed complementary slackness conditions, is positive or zero, so the dual feasibility conditions holds
Now the conditions have to be satisfied are the following
and the problem with inequality become the problem with equality subject to
It can be solved using Newton’s Method
Newton’s Method’s approximation becomes unstable if is too small and the current point is far from optimal.
So, we initially choose large and iteratively shrink it.
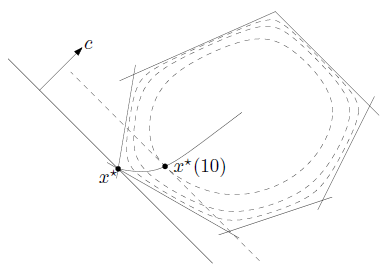
Analytic Central Point of Feasible Region
If is very large, then the optimization problem become the following. subject to
Since is a monotonic increasing function, the problem can be transformed as subject to
So, it finds the analytic central point of feasible region (gravity of the feasible region)
Phase 1 method
In the iteration, we have to find the initial points satisfying constraints satisfying
To ensure the condition, transform the optimization problem only at the initial stage. subject to
Now the problem can be solved using Infeasible Start Newton’s Method